Belgium is a fascinating country known for its rich history, diverse culture, and delectable cuisine. One of the most intriguing aspects of Belgium is its linguistic diversity. In this article, we will explore the languages spoken in Belgium, delving into their significance and the regions where they are predominantly used. As you navigate through this guide, you will gain a deeper understanding of Belgium's multilingual landscape, the historical context behind it, and its impact on the country's identity.
Belgium is home to three official languages: Dutch, French, and German. These languages reflect the country’s complex social fabric and regional distinctions. Each language has its own unique characteristics and cultural significance, making Belgium a true melting pot of languages.
In the following sections, we will break down the linguistic distribution across the regions of Belgium, provide insights into the historical background of these languages, and examine how they influence daily life, education, and government. So, let’s embark on this linguistic journey and discover what language is spoken in Belgium.
Table of Contents
Overview of Languages in Belgium
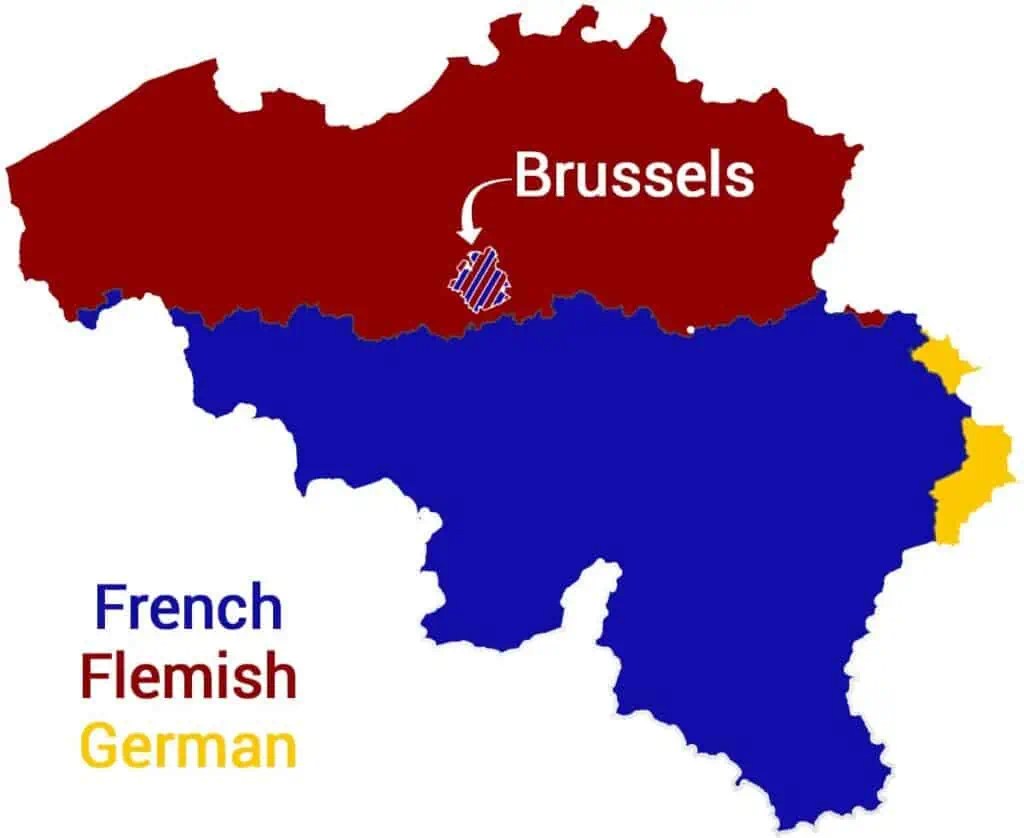
Belgium is divided into three main linguistic regions: Flanders, Wallonia, and the Brussels-Capital Region. Each of these regions has its predominant language:
- Dutch: Predominantly spoken in Flanders.
- French: Mainly spoken in Wallonia and parts of Brussels.
- German: Spoken by a small community in the eastern part of the country.
This linguistic division is not just a matter of communication; it plays a significant role in politics, culture, and social interactions within the country.
Dutch Language
Dutch is the most widely spoken language in Belgium, with approximately 60% of the population using it as their first language. It is primarily spoken in the northern region of Flanders, and it is also the language of instruction in many schools.
History and Development of Dutch in Belgium
The Dutch language, also known as Flemish in Belgium, has evolved over centuries. The influence of the Dutch language can be traced back to the medieval period, with significant developments occurring during the 16th and 17th centuries. The establishment of the Dutch language as a formal language in education and government has solidified its prominence in Belgium.
Characteristics of the Dutch Language
The Dutch language is known for its unique phonetics and vocabulary, which can vary significantly between Belgium and the Netherlands. Some distinguishing features include:
- Use of specific Flemish dialects.
- Differences in pronunciation and intonation.
- Distinctive vocabulary and expressions.
These variations contribute to the rich linguistic heritage of Belgium, making it an integral part of the nation's identity.
French Language
French is the second most spoken language in Belgium, with around 40% of the population using it as their primary language. It is predominantly spoken in the southern region of Wallonia and also has a significant presence in Brussels.
Historical Context of French in Belgium
The French language has deep historical roots in Belgium, particularly during the French rule in the late 18th century. The language gained prestige and was associated with education, culture, and the upper classes. Today, French is one of the official languages of Belgium and is widely used in government and media.
Unique Features of Belgian French
Belgian French has its own characteristics that set it apart from the French spoken in France. Some of these features include:
- Distinctive pronunciation, influenced by local dialects.
- Unique vocabulary and expressions not commonly used in France.
- Regional slang and idiomatic phrases.
These characteristics add to the cultural richness of the French language as spoken in Belgium.
German Language
German is the least spoken of the three official languages in Belgium, primarily used in a small community in the eastern part of the country, near the German border. Only about 1% of the population speaks German as their first language.
German-speaking Community in Belgium
The German-speaking community in Belgium has a unique cultural identity, with its own traditions and customs. This community is recognized as an official linguistic group and has its own government institutions.
Challenges and Opportunities for the German Language
Despite its small size, the German-speaking community faces challenges in preserving its language and culture. However, there are ongoing efforts to promote the German language in education and public life, ensuring its survival in Belgium.
Linguistic Diversity in Regions
Belgium's linguistic diversity is not just limited to its official languages. Numerous regional dialects and minority languages exist, adding to the country’s rich tapestry of languages. Some notable dialects include:
- Brabantian Dutch
- West Flemish
- Walloon
These dialects reflect the cultural and historical influences of various regions and contribute to the local identity of communities.
Language in Education
Language education in Belgium is structured around the country's linguistic divisions. Schools in Dutch-speaking regions primarily teach in Dutch, while schools in French-speaking regions use French as the medium of instruction. The presence of German-speaking schools ensures that the German language is also taught in its respective community.
Language Policies in Education
The Belgian government has implemented language policies to promote bilingualism and multilingualism among students. This is particularly important in Brussels, where both French and Dutch are commonly spoken. Educational institutions often encourage students to learn multiple languages, fostering a culture of linguistic diversity.
Language and National Identity
The languages spoken in Belgium are deeply intertwined with the country’s national identity. Language influences social interactions, cultural expressions, and political dynamics. The linguistic divide has historically led to tensions between communities, but it also fosters a rich cultural exchange.
The Role of Language in Belgian Culture
Language plays a vital role in shaping Belgian culture, from literature and music to cinema and art. Each language contributes to the country's cultural heritage, and events celebrating linguistic diversity are common throughout the year.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Belgium's linguistic landscape is a rich and complex tapestry woven from Dutch, French, and German languages. Each language carries its own history, significance, and cultural identity, shaping the lives of Belgians in various ways. Understanding what language is spoken in Belgium not only enriches our knowledge of the country but also highlights the importance of linguistic diversity in fostering social cohesion.
We invite you to share your thoughts in the comments below, explore more articles about Belgium, and continue your journey of discovery into this remarkable country.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you again soon as we continue to explore the wonders of language, culture, and identity.
Also Read
Article Recommendations


ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue9WiqZqko6q9pr7SrZirq2FlfLi0wK1kpZmenMKis8RmoKxlo6W8rLHNZqCnZZKauai11KZloaydoQ%3D%3D