The terminal velocity of a human is a fascinating concept that blends physics with human biology, making it a topic of interest for many. Understanding this phenomenon not only helps in grasping the laws of motion but also has practical implications in various fields, including skydiving, safety measures in free falls, and even in the study of extreme environments. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of terminal velocity, its calculations, and what factors influence it.
In the realm of physics, terminal velocity refers to the constant speed that an object eventually reaches when falling through a fluid, such as air. For human beings, this velocity is influenced by several factors, including body position, mass, and air resistance. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the various aspects that contribute to this speed and how it can affect a person's experience during free fall.
Whether you are a curious learner, a student of physics, or someone interested in skydiving, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights into the terminal velocity of a human. We will cover the science behind it, the factors that affect it, and real-life applications. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is Terminal Velocity?
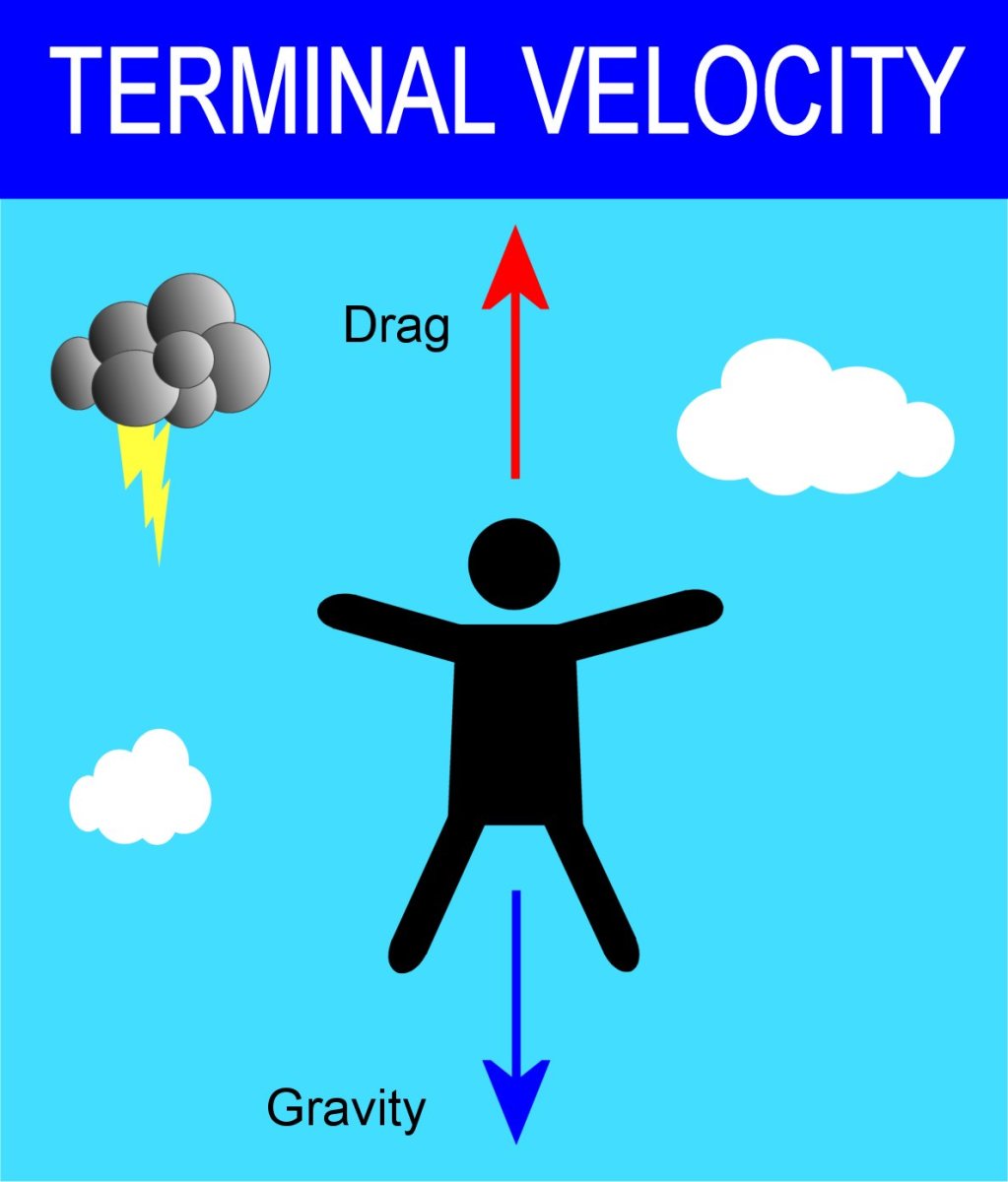
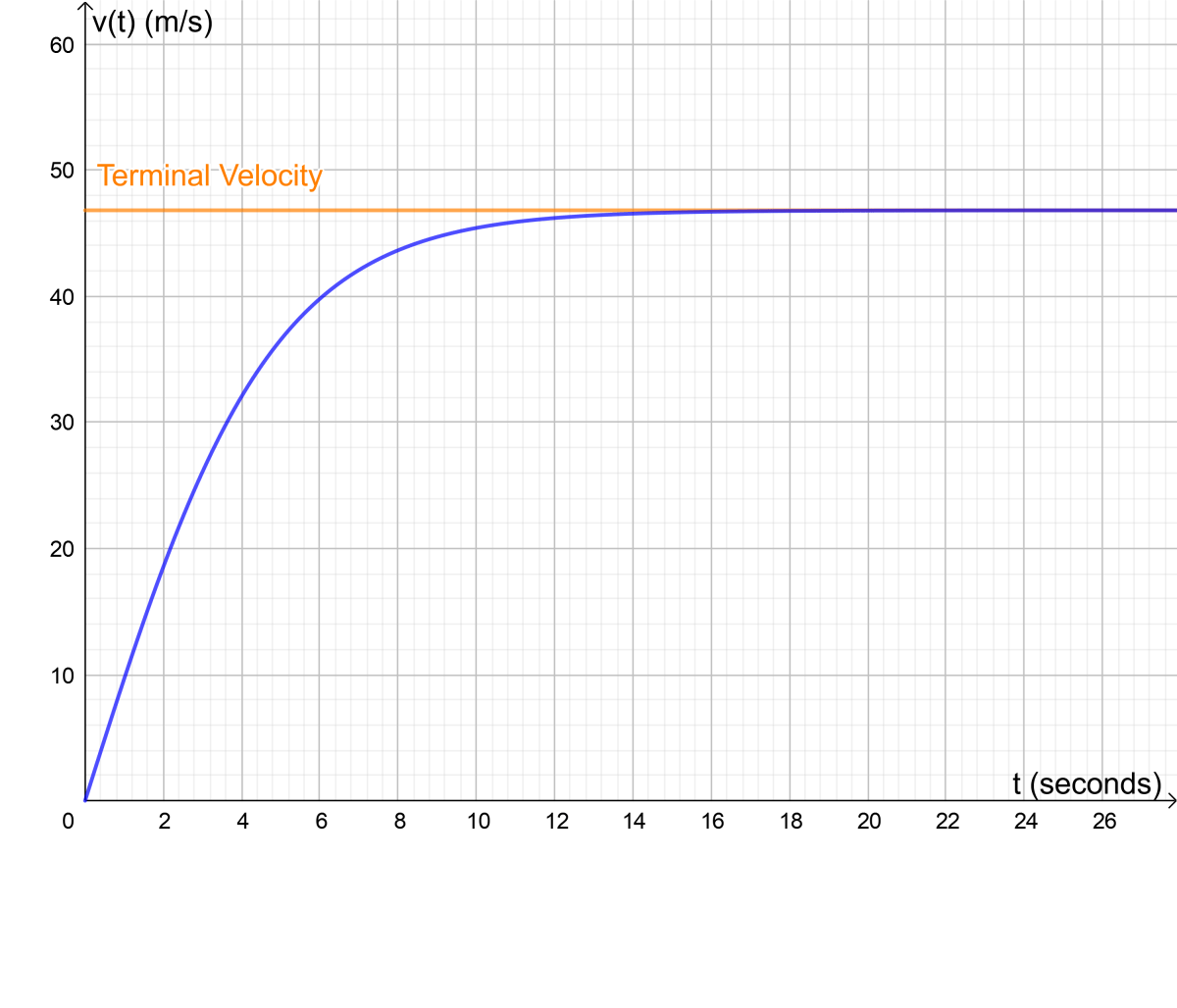
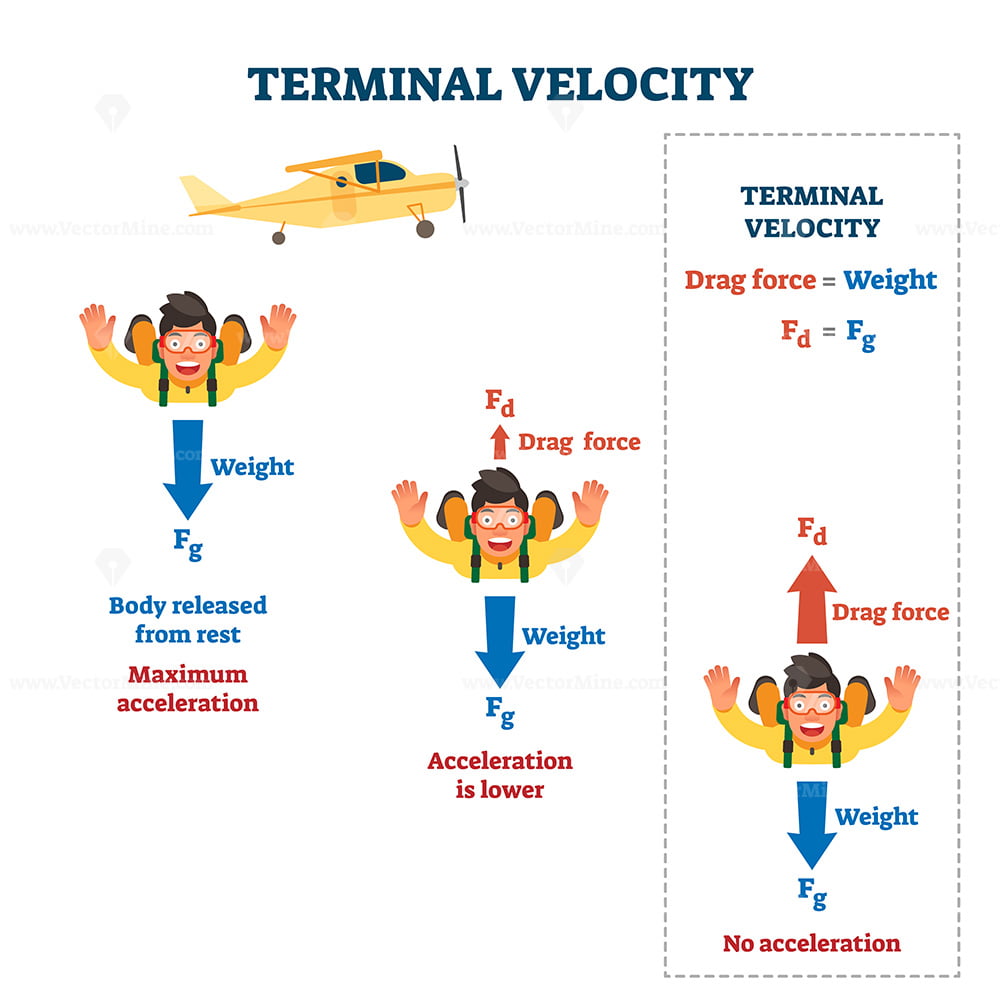
Terminal velocity is defined as the highest speed an object can reach when falling through a fluid. This occurs when the force of gravity pulling the object downward is balanced by the drag force (air resistance) acting upward. At this point, the object stops accelerating and continues to fall at a constant speed.
Physics Behind Terminal Velocity
The physics of terminal velocity can be explained using Newton's second law of motion. When an object is in free fall, it experiences two main forces: the gravitational force and the drag force. The gravitational force is constant and acts downward, while the drag force increases with speed until it equals the gravitational force.
Factors Affecting Terminal Velocity
Several factors influence the terminal velocity of a human, including:
- Mass: Heavier individuals will generally reach a higher terminal velocity due to the greater gravitational force acting on them.
- Body Position: The way a person positions their body while falling can significantly affect air resistance.
- Surface Area: A larger surface area increases drag, resulting in a lower terminal velocity.
- Altitude: At higher altitudes, air density is lower, which affects drag and terminal velocity.
Calculation of Terminal Velocity
The formula for calculating terminal velocity (Vt) is given by:
Vt = sqrt((2 * m * g) / p * A * Cd)
Where:
- m: Mass of the object (kg)
- g: Acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²)
- p: Density of the fluid (air) (kg/m³)
- A: Cross-sectional area of the object (m²)
- Cd: Drag coefficient (dimensionless)
Human Terminal Velocity
The terminal velocity of a human varies but is typically around 53 m/s (approximately 120 mph) when in a belly-to-earth position. However, this speed can change depending on the individual's body position and other factors discussed earlier.
Variations in Terminal Velocity
When a person falls with their feet or head first, the terminal velocity can increase significantly, reaching speeds of up to 90 m/s (about 200 mph) due to a smaller cross-sectional area and reduced drag.
Impact of Body Position on Terminal Velocity
The position of a body during free fall greatly affects terminal velocity. The two main positions are:
- Belly-to-Earth: This position offers maximum surface area and results in a lower terminal velocity.
- Feet or Head First: This position minimizes drag, leading to a higher terminal velocity.
Real-Life Applications of Terminal Velocity
Understanding terminal velocity has several practical applications:
- Skydiving: Knowledge of terminal velocity helps skydivers plan their jumps and safety measures.
- Parachuting: Parachute designs take terminal velocity into account to ensure a safe landing.
- Emergency Services: Rescue operations in high-altitude scenarios consider terminal velocity for safety.
Safety Measures in Free Falls
To ensure safety during free falls, several measures are taken:
- Use of Parachutes: Parachutes are designed to increase drag significantly, reducing terminal velocity during descent.
- Training: Skydivers undergo training to position their bodies correctly during free fall.
- Safety Gear: Proper gear is essential to minimize injuries in case of emergency landings.
Conclusion
In summary, the terminal velocity of a human is a critical concept that encompasses various scientific principles and practical applications. Factors such as mass, body position, and air resistance play significant roles in determining the terminal velocity experienced by an individual during free fall. By understanding these elements, one can appreciate the complexities of falling through the air and the importance of safety measures in extreme situations.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts in the comments below, share this article with others, or explore more topics on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again soon!
Also Read
Article Recommendations
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue9KtmKtlpJ64tbvKcWawoJGpeqq%2FjK2fnmWkmr%2Butc2ao2aulaG8pLXTsmSonl2WeqnBzJqlZ6Ckork%3D