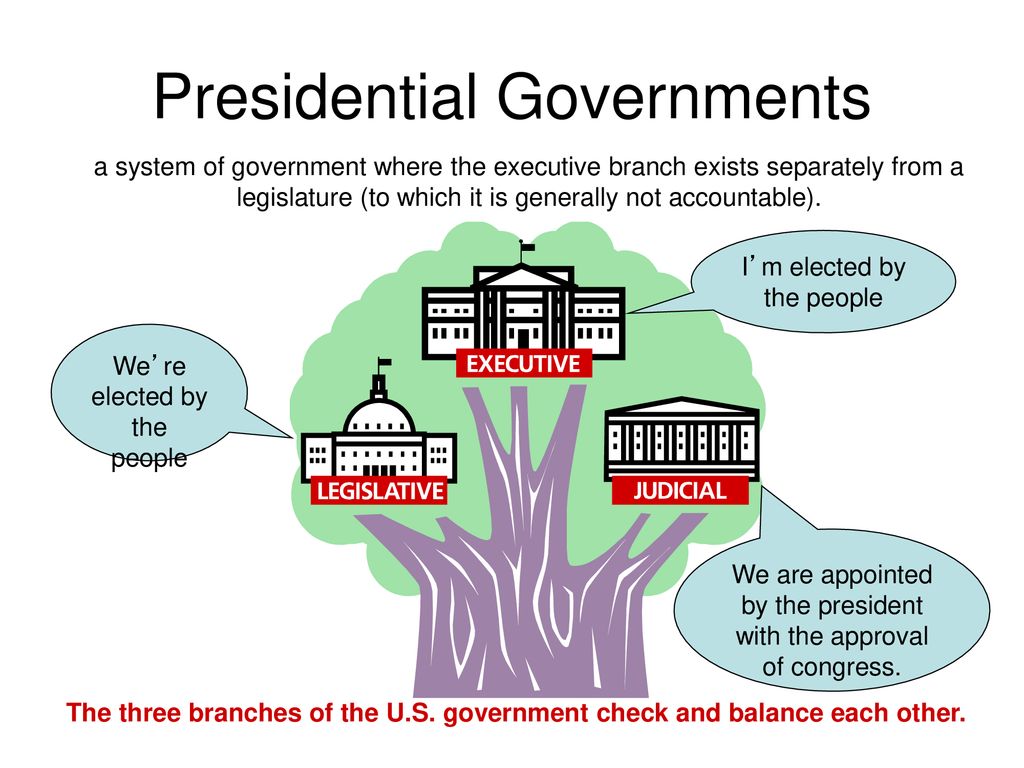
Presidential governments represent a distinctive form of political structure characterized by the separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. In this system, the President serves as both the head of state and the head of government, wielding significant authority over the administration and policymaking processes. This unique arrangement fosters a dynamic interaction between various branches of government, establishing a framework for governance that is both robust and complex. The implications of this system extend beyond mere political mechanics, influencing the very fabric of governance in countries around the globe.
In many presidential governments, the President is elected directly by the populace, granting them a democratic mandate that further legitimizes their authority. This electoral process contrasts sharply with parliamentary systems, where the head of government is typically a member of the legislative branch and is chosen by fellow lawmakers. The concentration of power in the hands of a single individual can lead to efficient decision-making, but it also raises concerns about potential overreach and the erosion of checks and balances.
The evolution of presidential governments has been shaped by historical, cultural, and social factors that differ widely from one nation to another. As we explore the intricacies of this system, it becomes evident that understanding presidential governments requires not only an examination of their structural elements but also an appreciation for the diverse contexts in which they operate. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics, advantages, and challenges associated with presidential governments, providing a nuanced perspective on their role in contemporary governance.
What Are the Key Features of Presidential Governments?
Presidential governments are defined by several key features that distinguish them from other forms of governance, such as parliamentary systems. These include:
- The President's dual role as both head of state and head of government.
- A clear separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
- A fixed term for the President, which provides stability and continuity.
- The ability of the President to veto legislation, providing a check on the legislative branch.
How Do Presidential Governments Function in Practice?
The functioning of presidential governments varies significantly across different countries, influenced by specific constitutional frameworks and political cultures. In practice, the President often has considerable authority over executive orders, military decisions, and foreign policy. However, this power is tempered by the necessity of legislative approval for budgetary matters and significant policy changes.
What Are the Advantages of Presidential Governments?
Presidential governments offer several advantages that can enhance governance and political stability:
- Direct Accountability: Presidents are elected by the people, fostering a direct line of accountability.
- Decisive Leadership: A single executive can make swift decisions, especially in times of crisis.
- Stability: Fixed terms for Presidents can provide stability and predictability in governance.
What Challenges Do Presidential Governments Face?
Despite their advantages, presidential governments are not without challenges. Some of the most pressing issues include:
- Risk of Authoritarianism: Concentration of power in the presidency can lead to authoritarian tendencies.
- Gridlock: A divided government can impede legislative progress and lead to political stalemate.
- Impeachment Risks: The potential for impeachment can create political instability and uncertainty.
Are Presidential Governments Compatible with Democracy?
The relationship between presidential governments and democracy is complex. While many presidential systems are democratic, others can devolve into authoritarian regimes. The key to maintaining a healthy democracy within a presidential government lies in the strength of institutions and the rule of law. Effective checks and balances, an independent judiciary, and a vibrant civil society are essential components that safeguard democratic principles.
How Do Different Countries Implement Presidential Governments?
Presidential governments manifest uniquely across different countries. For instance:
- In the United States, the President has significant powers, including veto authority and military command.
- In Brazil, the President also enjoys considerable powers but faces challenges from a fragmented legislature.
- In Nigeria, the presidential system is influenced by ethnic diversity and regional politics, affecting governance.
What Role Do Elections Play in Presidential Governments?
Elections are a cornerstone of presidential governments, serving as a mechanism for accountability and representation. The electoral process varies significantly, with some countries employing direct popular votes, while others may have electoral colleges or parliamentary approval. The integrity of the electoral process is crucial for the legitimacy of the presidential office.
Conclusion: The Future of Presidential Governments
In conclusion, presidential governments play a vital role in shaping political landscapes across the globe. Their unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges continue to evolve in response to changing societal dynamics. As we move forward, the effectiveness of presidential systems will depend on the ability of governments to adapt, ensuring that democratic principles are upheld and that power is exercised responsibly.
Also Read
Article Recommendations


ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue9Cupq2do6OyuL%2BQbWapqpWotqWxza2gmqRdnLy3sdGnpJ6mpKh7qcDMpQ%3D%3D