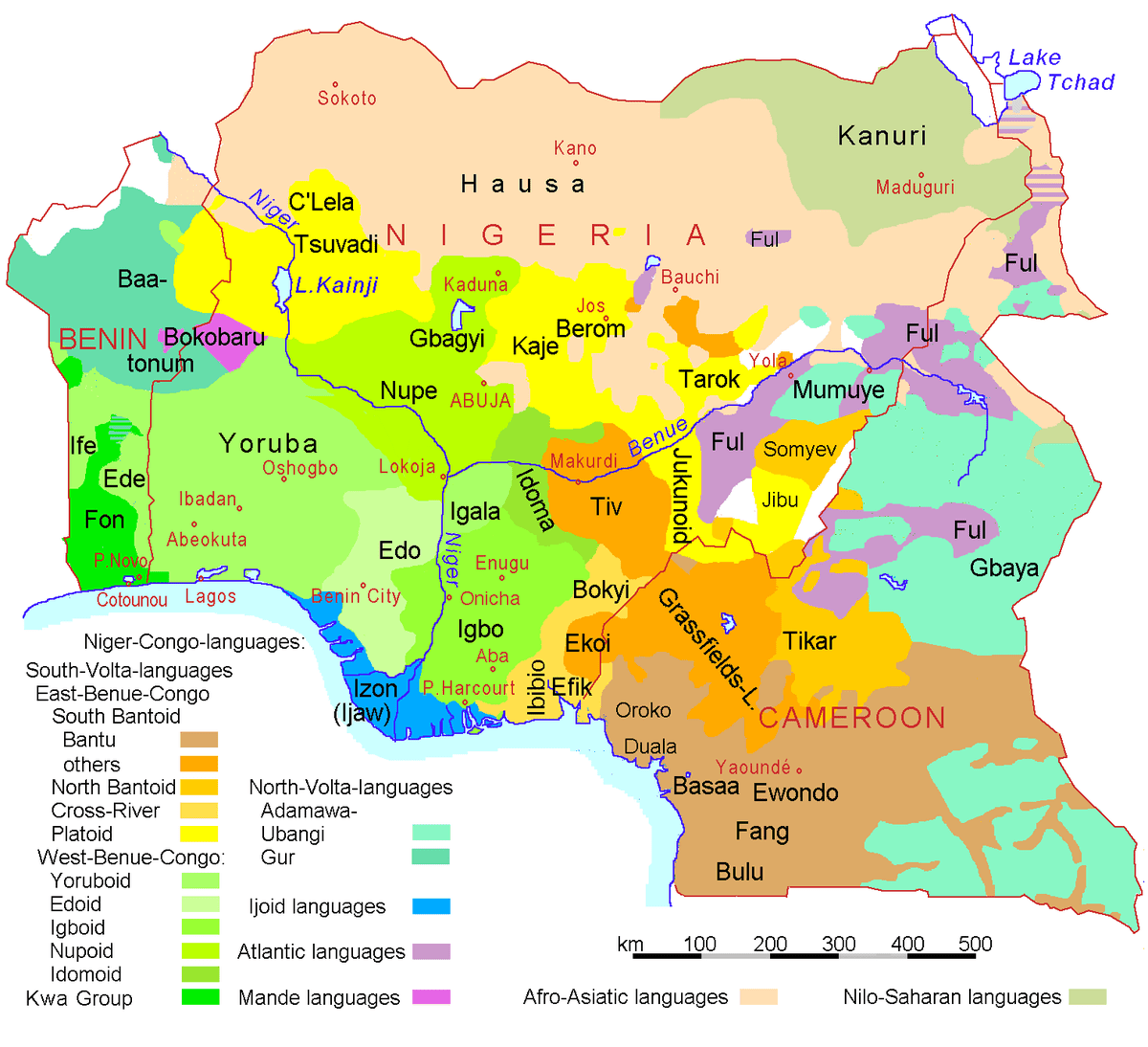
Nigeria is a country renowned for its rich tapestry of cultures and languages. With over 500 distinct languages spoken across its diverse regions, Nigeria stands as one of the most linguistically varied nations in the world. This linguistic diversity is not just a reflection of the multitude of ethnic groups that inhabit the land but also a testament to the country's complex history and social dynamics. Understanding what language is spoken in Nigeria is essential for grasping the nation's cultural identity and heritage.
The most widely spoken language in Nigeria is Hausa, primarily in the northern regions, followed closely by Yoruba and Igbo, which dominate the southwestern and southeastern areas, respectively. However, these languages represent only a fraction of the linguistic landscape. Each ethnic group, from the Fulani to the Ijaw, contributes its unique dialects and languages, enriching the overall communicative fabric of the nation.
The significance of language in Nigeria extends beyond mere communication; it plays a crucial role in shaping social interactions, cultural expressions, and even political discourse. In a country as vast and diverse as Nigeria, knowing what language is spoken in Nigeria can create pathways for deeper understanding and appreciation of its people and their traditions.
What are the Major Languages Spoken in Nigeria?
Nigeria boasts a plethora of languages, but some stand out due to their widespread use and cultural importance. The three most prominent languages are:
- Hausa: Predominantly spoken in the northern states, Hausa serves as a lingua franca among various ethnic groups.
- Yoruba: This language is a major language in the southwest and is known for its rich oral traditions and proverbs.
- Igbo: Widely spoken in the southeastern region, Igbo is characterized by its numerous dialects and vibrant cultural expressions.
What Role Does Language Play in Nigerian Identity?
Language in Nigeria is more than just a means of communication; it is a vital part of individual and collective identity. Each ethnic group has its language that embodies its history, beliefs, and way of life. Language fosters a sense of belonging and community, allowing individuals to connect with their roots and heritage. Furthermore, the use of indigenous languages in education and media has gained momentum, promoting cultural pride and awareness.
How Many Languages Are Spoken in Nigeria?
Nigeria is home to an astonishing number of languages, with estimates ranging from 500 to over 700 distinct languages. This linguistic diversity is influenced by the country's various ethnic groups, each with its unique language. The Ethnologue, a comprehensive reference work cataloging all of the world's known living languages, lists around 526 languages for Nigeria, showcasing the richness of its linguistic heritage.
What Language is Used in Education and Government?
While indigenous languages are vital for cultural preservation, English serves as the official language of Nigeria. It is widely used in government, education, and formal communication. The adoption of English as a medium of instruction in schools has facilitated access to education, although there is a growing movement advocating for the inclusion of local languages in the curriculum to promote bilingualism and cultural awareness.
Is There a Language Policy in Nigeria?
Yes, Nigeria has a language policy that aims to promote multilingualism and the use of indigenous languages. The National Policy on Education emphasizes the importance of using the mother tongue as the medium of instruction in the early years of education. However, the implementation of this policy faces challenges, including limited resources and varying levels of government support across different states.
What Challenges Do Indigenous Languages Face in Nigeria?
Despite the linguistic wealth of Nigeria, indigenous languages face numerous challenges that threaten their survival:
- Urbanization: The migration of people to urban areas often leads to a decline in the use of indigenous languages as English becomes the dominant mode of communication.
- Globalization: The influence of global media and technology has further entrenched the use of English, overshadowing local languages.
- Lack of Resources: Many indigenous languages lack formal documentation, educational materials, and media representation, making it difficult for younger generations to learn and use them.
What Efforts Are Being Made to Revitalize Indigenous Languages?
In response to the declining use of indigenous languages, various initiatives are underway to promote and revitalize them. These include:
- Community Programs: Local organizations and communities are working to create awareness about the importance of preserving their languages through workshops, storytelling sessions, and cultural events.
- Educational Initiatives: Some schools are beginning to incorporate indigenous languages into their curricula, fostering pride and interest among students.
- Media Representation: The rise of local content in radio, television, and online platforms has provided a space for indigenous languages to thrive and gain visibility.
Conclusion: What Language is Spoken in Nigeria?
In summary, Nigeria is a vibrant mosaic of languages, each contributing to the country's rich cultural heritage. Understanding what language is spoken in Nigeria is not just about identifying the major languages; it is about recognizing the intricate relationships between language, identity, and community. As efforts to preserve and revitalize indigenous languages continue, there is hope for future generations to embrace their linguistic heritage while navigating an increasingly globalized world.
Also Read
Article Recommendations
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue9OrsJ6bmKR%2BenvWoZitZZyWu6jBwKCcZqGjYsCxu8qepWahnmK7qrPEq6CaZpipuq0%3D